Danke für dein Feedback.
ROCKPro64 - RTC
-
Unser ROCKPro64 hat eine RTC (RealTimeClock), so wie jeder ausgewachsene PC kann man diese Uhr mit einer Batterie puffern. So wie die BIOS Batterien in Euren PCs.
Dazu hat der ROCKPro64 einen Anschluss auf dem Board.
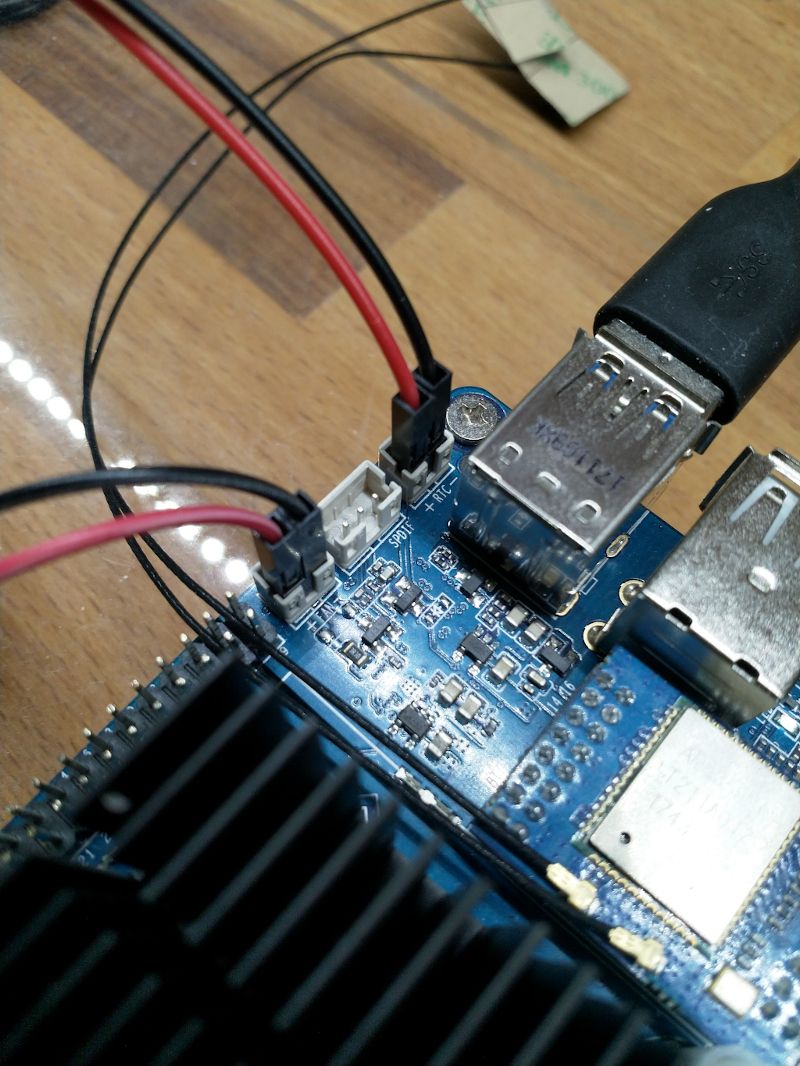
An RTC + und - wird die Batterie (CR1220-3V) angeschlossen. Hier der entsprechende Schaltplan. Auf Seite 18 unter PMIC RK808-D findet ihr die RTC Schaltung.
Wenn man jetzt den ROCKPro64 ohne Netzwerkverbindung startet schaut man sich mal die RTC an.
root@rockpro64:~# dmesg | grep rtc [ 4.798978] rk808-rtc rk808-rtc: registered as rtc0 [ 4.807268] OF: graph: no port node found in /i2c@ff3d0000/typec-portc@22 [ 5.032372] rk808-rtc rk808-rtc: setting system clock to 2013-01-18T14:13:22)Nun stellen wir die RTC nach der Systemzeit.
hwclock -wKontrollieren
root@rockpro64:~# timedatectl Local time: Sat 2020-05-09 16:09:29 CEST Universal time: Sat 2020-05-09 14:09:29 UTC RTC time: Sat 2020-05-09 14:09:30 Time zone: Europe/Berlin (CEST, +0200) System clock synchronized: no NTP service: inactive RTC in local TZ: noOk, nun ist die Systemzeit gleich der RTC. Danach neustarten.
Zeit erneut kontrollieren.
root@rockpro64:~# dmesg | grep rtc [ 4.804679] rk808-rtc rk808-rtc: registered as rtc0 [ 4.812980] OF: graph: no port node found in /i2c@ff3d0000/typec-portc@22 [ 5.059011] rk808-rtc rk808-rtc: setting system clock to 2020-05-09T14:10:27)Die RTC hat nun die Zeit, die wir gesetzt hatten. Ich denke, das sollte so passen. Wenn nicht, und ich schreibe hier Blödsinn, bitte korrigieren!
-
-
-
linux-mainline-u-boot
Angeheftet Images -
-
-
DTS DTB Files bearbeiten
Angeheftet ROCKPro64 -
stretch-minimal-rockpro64
Verschoben Linux -
Serielle Konsole UART2
Angeheftet Verschoben Hardware